# LangGraph 使用案例
# 普通的langgraph案例
// 定义 graph 的流程的数据结构:有一个 string[] 类型的 channel -> list
// 默认值是空数组,state 更新的逻辑是数组拼接,但是去重
const TestStateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
list: Annotation<string[]>({
default: () => [],
reducer: (current, updated) => {
return Array.from(new Set(current.concat(updated)));
}
})
});
const graphBuilder = new StateGraph(TestStateAnnotation);
const node1 = (_state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
return {
list: ["a", "b", "cc"]
};
};
const node2 = (_state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
return {
list: ["cc", "ddd"]
};
};
// 添加三个节点
const node3Action = (_state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
return {
list: ["a", "ee"],
name: 222 // 注意这里多返回了一个 222
};
};
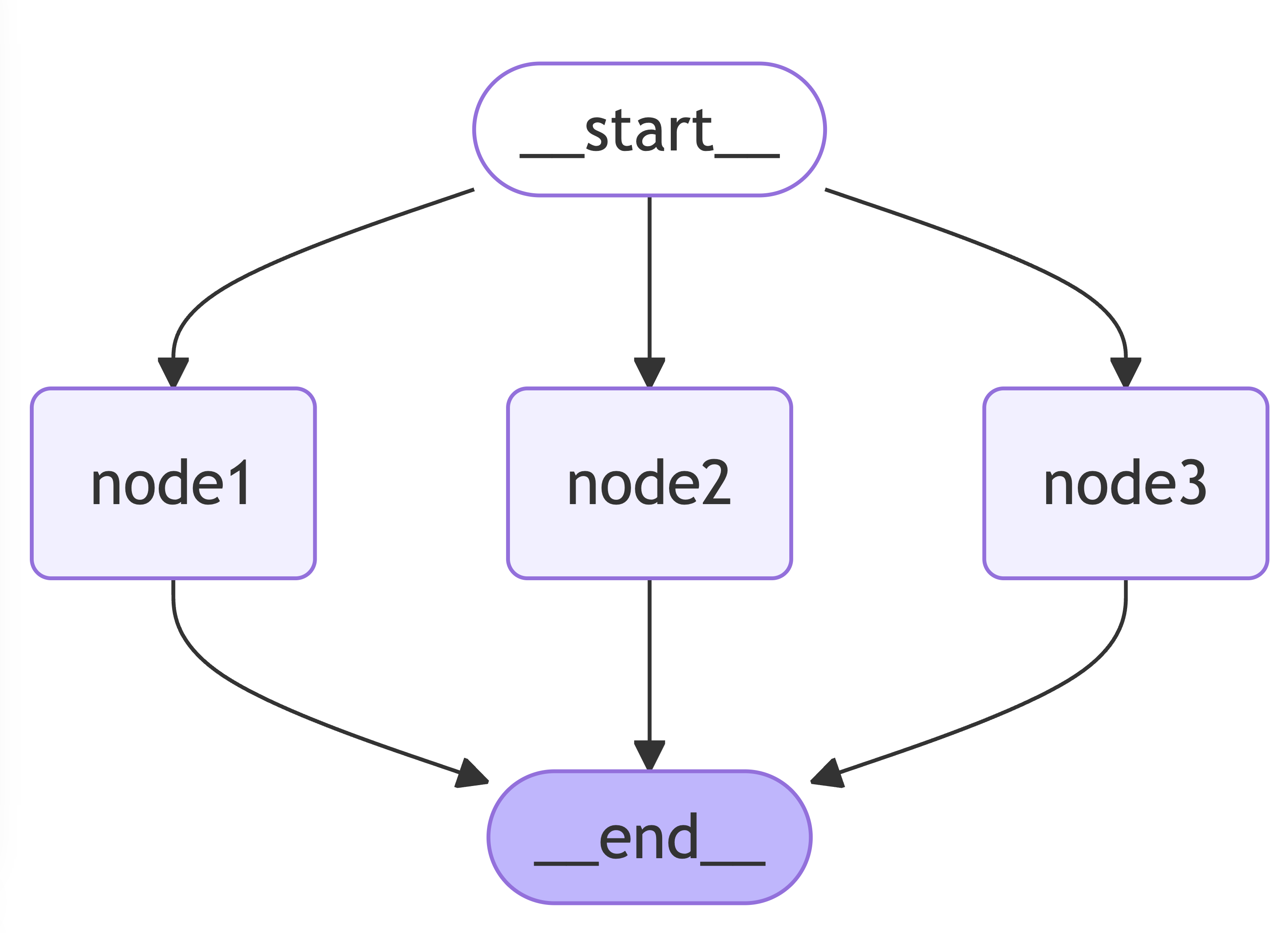
graphBuilder.addNode("node1", node1);
graphBuilder.addNode("node2", node2);
graphBuilder.addNode("node3", node3Action);
graphBuilder.addEdge(START, "node1");
graphBuilder.addEdge(START, "node2");
graphBuilder.addEdge(START, "node3");
graphBuilder.addEdge("node1", END);
graphBuilder.addEdge("node2", END);
graphBuilder.addEdge("node3", END);
# 条件分支
addConditionalEdges(source, routingFunction, pathMap?): this
- source: 源节点
- routingFunction: 路由函数,根据返回值决定流向
- pathMap: 可选,用于明确 routingFunction 每个返回值的流向,不指定则默认增加一个 end 的边
pathMap 可以是一个 string map 或者 string[],如果是 string map,则表示node 的 map 结构,否则如果是一个数组类型,代表当前条件路由允许到达的节点。
# 条件edge 的langgraph案例
如果没有通过 pathMap 明确 routingFunction 每个返回值的流向,LG 会默认为条件分支增加一个 end 的边。
// 如果没有通过 pathMap 明确 routingFunction 每个返回值的流向,LG 会默认为条件分支增加一个 __end__ 的边。
const condition = (state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
// 一个模拟条件,假设存在a了就走node2,否则走node3
if (state.list.includes("a")) {
return "node2";
} else {
return "node3";
}
};
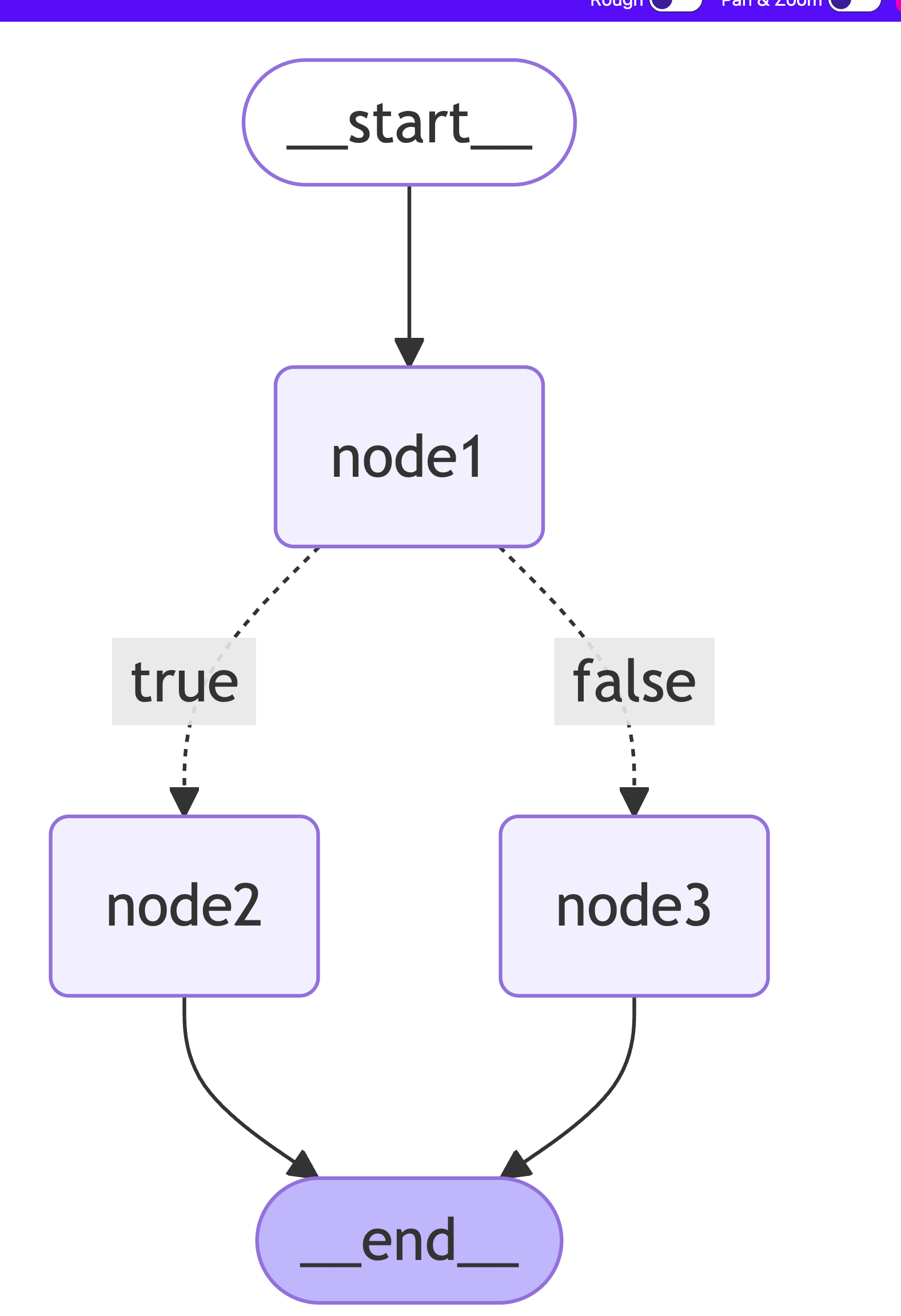
graphBuilder.addNode("node1", node1);
graphBuilder.addNode("node2", node2);
graphBuilder.addNode("node3", node3Action);
graphBuilder.addEdge(START, "node1");
graphBuilder.addConditionalEdges("node1", condition, {
node2: "node2",
node3: "node3"
});
graphBuilder.addEdge("node2", END);
graphBuilder.addEdge("node3", END);
# 条件edge + 并行节点 的langgraph案例
如果没有通过 pathMap 明确 routingFunction 每个返回值的流向,LG 会默认为条件分支增加一个 end 的边。
const condition = (state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
if (state.list.includes("a")) {
return END;
} else {
return ["node2", "node3"];
}
};
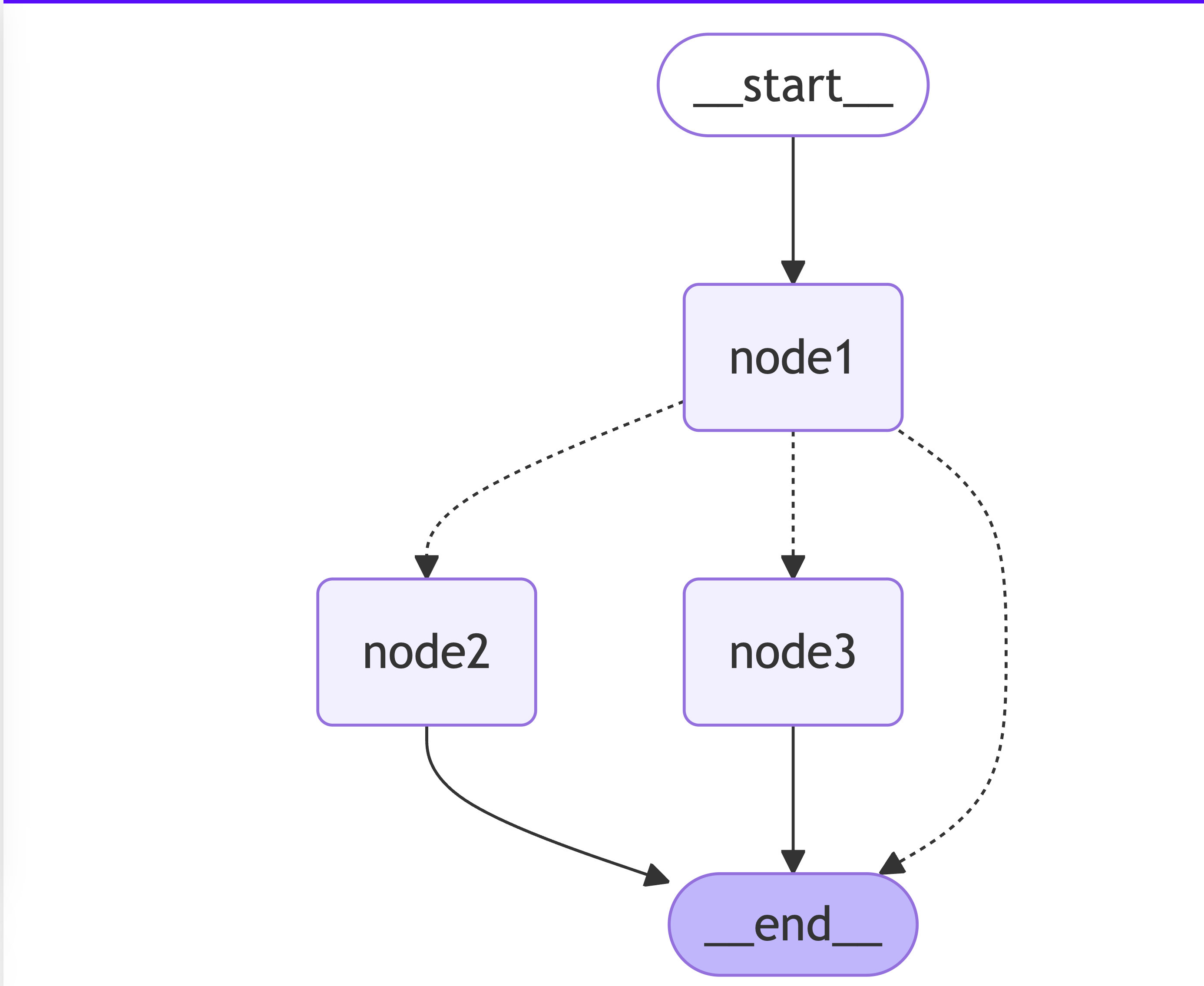
graphBuilder.addNode("node1", node1);
graphBuilder.addNode("node2", node2);
graphBuilder.addNode("node3", node3Action);
graphBuilder.addEdge(START, "node1");
graphBuilder.addConditionalEdges("node1", condition);
graphBuilder.addEdge("node2", END);
graphBuilder.addEdge("node3", END);
# 并行、循环节点
在 前面的代码 中,我们可以基于 addConditionalEdges() 方法,辅助我们实现并行任务的能力,我们已经实现了简单的并行任务
const condition = (state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
if (state.list.includes("a")) {
return END;
} else {
return ["node2", "node3"];
}
};
但是此时我们只能固定 node2 和 node3 一起执行,无法动态的复用多个节点,而且这个过程也不是可循环的(这里循环是指多次执行同一个节点)。
# 利用 Send 实现并行
Send 在 LG 中是一个 Class,我们可以实例化,并且构造函数很简单:
- node:要路由到哪个节点
- args:路由到节点时,传递给节点的参数是什么(可以传入整个 state 也可以传入独立的参数)
我们想要实现的效果:
- 输入:["langgraph"]
- 输出:{"langgraph": ['l', 'a', 'n', 'g', 'g', 'r', 'a', 'p', 'h']}
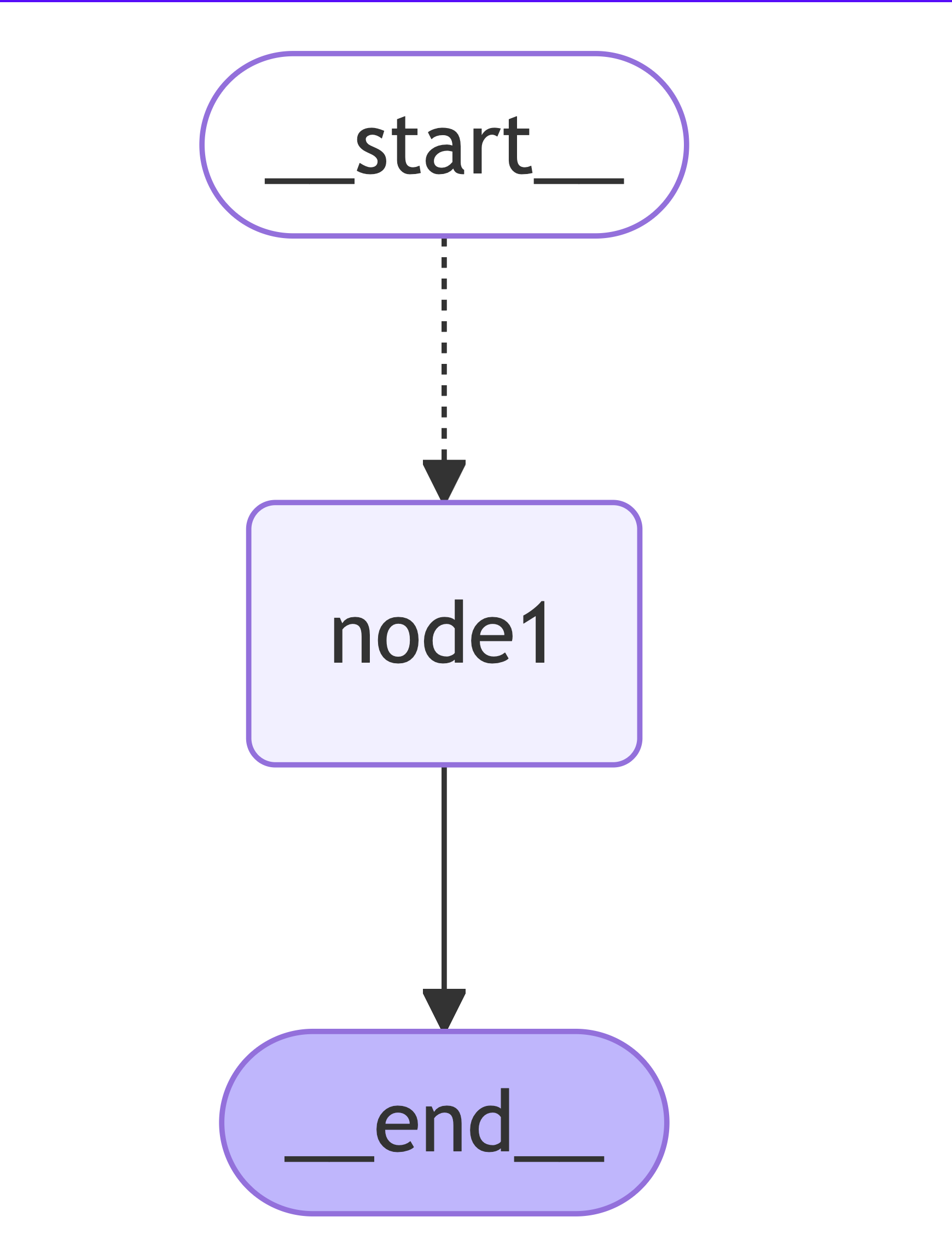
整体思路:动态创建 N 个 edge,路由到【字符串处理】(如下面的Node1)这个节点上,并行执行,然后收集结果;(并行)
我们观察流程图,虽然只有一条线 start -> node1 -> end , 但是我们知道这个过程中 node1 会并行的执行 N 次。
const nodeAction = (str: string) => {
// 因为 node1 每次返回的 State 类型是是 { output : Record<string, string[]> },可以通过我们的 reducer 直接合并成最终的结果
return {
output: { [str]: Array.from(str) }
};
};
const condition = (state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
const { inputList } = state;
// 创建多个节点
return inputList.map(item => new Send("node1", item));
};
graphBuilder.addNode("node1", nodeAction);
graphBuilder.addConditionalEdges(START, condition, ["node1"]);
graphBuilder.addEdge("node1", END);
# 利用 Send 实现循环
我们想要实现的效果:
- 输入:["langgraph"]
- 输出:{"langgraph": ['l', 'a', 'n', 'g', 'g', 'r', 'a', 'p', 'h']}
整体思路:非并行循环:我们再输入 state 之后,将 state 传递到节点,节点自己循环自己,最终完成任务,输出结果;(非并行,无法利用现有的 node,因为现有的 node 只接受 string 入参)
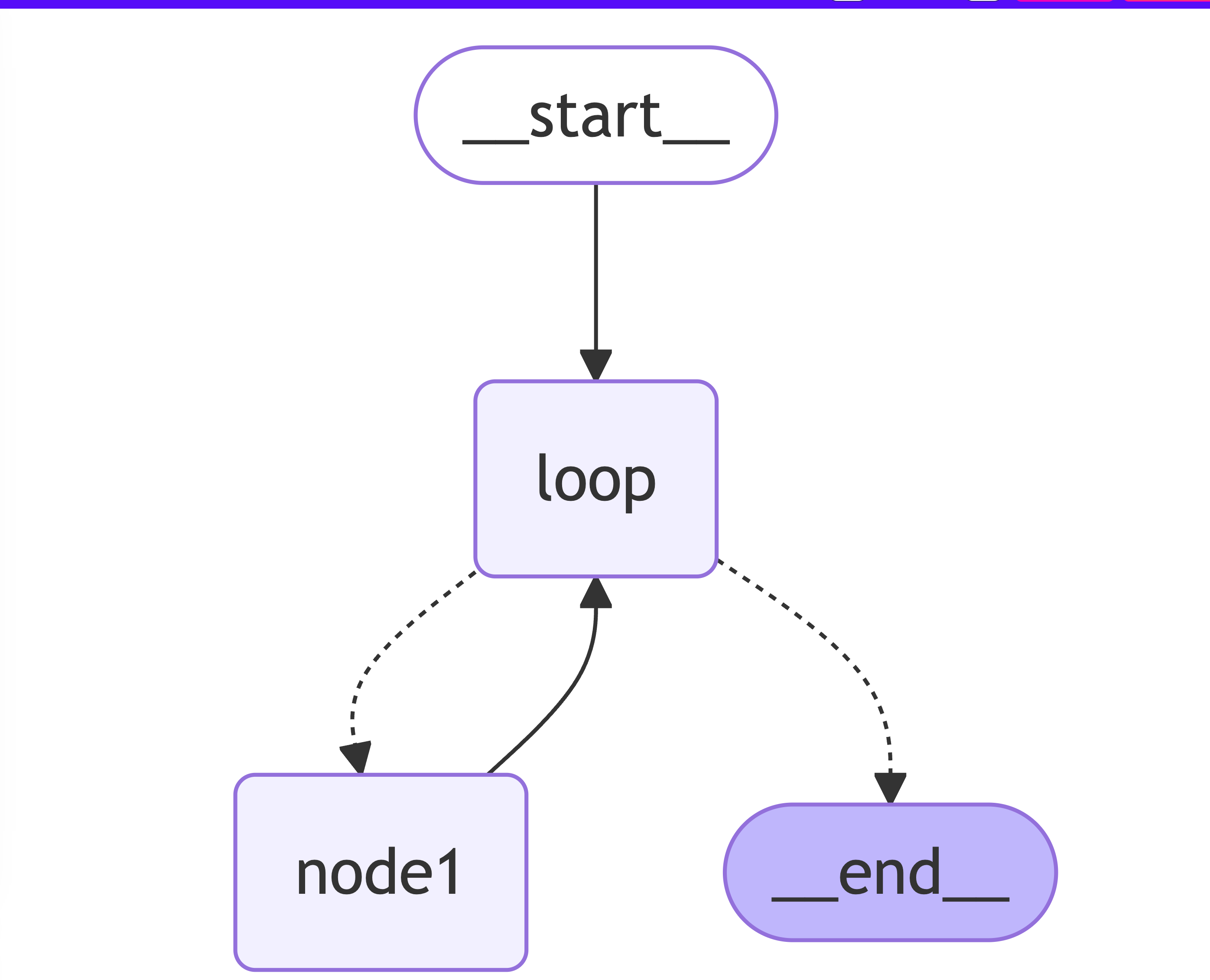
流程中循环的实现其实就是一个节点执行完成后,重新回到某个起点,然后通过某个条件判断是否要结束,转到另外一个节点
注意
- Send 不允许直接指向 end 节点
- Send 不允许直接指向 start 节点
const nodeAction = (str: string) => {
// 并且因为 node1 每次返回的 State 类型是是 { output : Record<string, string[]> },可以通过我们的 reducer 直接合并成最终的结果。
return {
output: { [str]: Array.from(str) }
};
};
const loopNode = (state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
return state;
};
const condition = (state: typeof TestStateAnnotation.State) => {
const { inputList } = state;
const first = inputList.shift();
if (!first) {
return END;
}
return new Send('node1', first);
};
graphBuilder
.addNode('node1', nodeAction)
.addNode('loop', loopNode)
.addEdge(START, 'loop')
.addConditionalEdges('loop', condition, ['node1', END])
.addEdge('node1', 'loop');
# State 的修改
我们声明的 State 会在流程的各个节点流转,每个节点都可以进行 state 更改,我们通过 reducer 决定数据更改的方式,默认的 state 会通过覆盖的方式不断被修改。
# State 的合并
当业务应用复杂的时候,我们可能会有多个 Annotation.Root 声明的 State,或者我们希望复用某些 State Annotation,LG 支持我们通过state 的 spec 属性进行合并。 下面的示例中,我们新增了一个 AnotherStateAnnotation 然后我们将前面的 StateAnnotation 和 AnotherStateAnnotation 合并成一个新的 mergedStateAnnotation。
const AnotherStateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
title: Annotation<string>,
});
const mergedStateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
...StateAnnotation.spec,
...AnotherStateAnnotation.spec,
});
# State 自动忽略
通过 Annotation.Root 声明了 State 之后,得到三个属性(channel):name、list、age 意味着我们可以在流程中修改这3个属性的值,因为每个属性是一个 channel,因此当 state 输入到节点中时:
- 如果节点只修改了其中某个属性,其他的属性会保持不变,不会丢失;
- 如果节点修改了没有在 Annotation.Root 中声明的属性,则不会生效
参考下面案例:
const StateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
name: Annotation<string>,
list: Annotation<Record<string, string[]>>({
reducer: (current, updated) => ({ ...current, ...updated }),
}),
age: Annotation<number>({
default: () => 1,
reducer: current => current + 1,
}),
});
const graphBuilder = new StateGraph(StateAnnotation);
const nodeAction = () => {
return {
name: 'node1',
title: 'not existed channel',
};
};
graphBuilder.addNode('node1', nodeAction).addEdge(START, 'node1').addEdge('node1', END);
const graph = await graphBuilder.compile();
const res = await graph.invoke({ list: ['xxx'] });
- list 和 age我们没有在 node1 节点中返回,么有处理,因此保持不变;
- name 是 node1 赋值的
- title 虽然 node1 返回了,但是我们没有声明这个 channel,因此结果中也不会存在这个属性
# 输出输出使用不同State
const InAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
question: Annotation<string>,
});
const OutAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
answer: Annotation<string>,
});
// 使用不同的 State
const graphBuilder = new StateGraph({
input: InAnnotation,
output: OutAnnotation,
});
const nodeAction = (state: typeof InAnnotation.State) => {
this.logger.info('state', state);
return {
answer: 'my name is zhanwen li',
duration: 3000,
question: state.question,
};
};
graphBuilder.addNode('node1', nodeAction).addEdge(START, 'node1').addEdge('node1', END);
const graph = await graphBuilder.compile();
const res = await graph.invoke({ question: "what's your name?", user: 'zhanwen' });
上面的代码输出为 {"answer": 'my name is zhanwen li'}
# 总结
LangGraph 流程的 state 设计中,所有的 state 属性都会变成一个 channel,任何节点都能通过 channel 修改 state 的值。 一个节点只能读取通过 Annotation.Root 声明过的 state channel,如果某个 channel 没有声明,则 node 节点无法直接读取值,但仍然可以修改它。
# 使用 ToolNode + Agent 实现简单的天气查询
ToolNode 是 LangGraph 中一种特殊的节点,用来帮助我们集合 tool calling 实现第三方服务集成,构建 Agent 应用。 在基于 LangGraph 实现的应用中,ToolNode 帮助我们衔接 模型决策与动作执行
- 意图识别:ToolNode 会读取 LLM tool calling 后返回的消息(AIMessage),消息中会包含 tool calling 的结论和参数提取; 根据 tool 的描述,决定调用哪个 tool(可能有 N 个tool)
- 参数提取:ToolNode 基于提供的工具列表,实际上触发工具的 invoke 方法,并且传入模型提取的参数
分析一下下面的流程:
- 我们定义了一个
getWeather的工具,这个工具会根据输入的 location 返回天气信息; - 使用 OpenAI 的 gpt-3.5-turbo LLM模型,作为agent Node;
- 用户 输入
what is the weather in SF - 先经过 agent node ; 得到AI Message; 即获取到定位信息为 San Francisco
- 然后经过 tools node; 触发
getWeather工具,传入参数为 San Francisco;最终得到天气信息为 It's 60 degrees and foggy. - 由于 edge 定义,tool 执行后,下一个为 agent , 将工具的结果返回给 LLM 模型,触发 LLM 模型的第二次调用
- 此时 LLM 模型的输入为 It's 60 degrees and foggy. LLM 结合上下文信息,得到最终的结果为
The weather in San Francisco is currently 60 degrees and foggy.
export async function main() {
// 手动顶一个tool
const getWeather = tool(
input => {
if (["sf", "san francisco"].includes(input.location.toLowerCase())) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy.";
} else {
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny.";
}
},
{
name: "get_weather",
description: "Call to get the current weather.",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("Location to get the weather for.")
})
}
);
const tools = [getWeather];
const modelWithTools = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature: 0,
maxTokens: 600
}).bindTools(tools);
// 工具的集合
const toolNodeForGraph = new ToolNode(tools);
const shouldContinue = (state: typeof MessagesAnnotation.State) => {
const { messages } = state;
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1];
// 如果AI Message 里有 tool_calls,就进入 tools 节点 去处理
if ("tool_calls" in lastMessage && Array.isArray(lastMessage.tool_calls) && lastMessage.tool_calls?.length) {
return "tools";
}
return "__end__";
};
const callModel = async (state: typeof MessagesAnnotation.State) => {
const { messages } = state;
const response = await modelWithTools.invoke(messages);
return { messages: response };
};
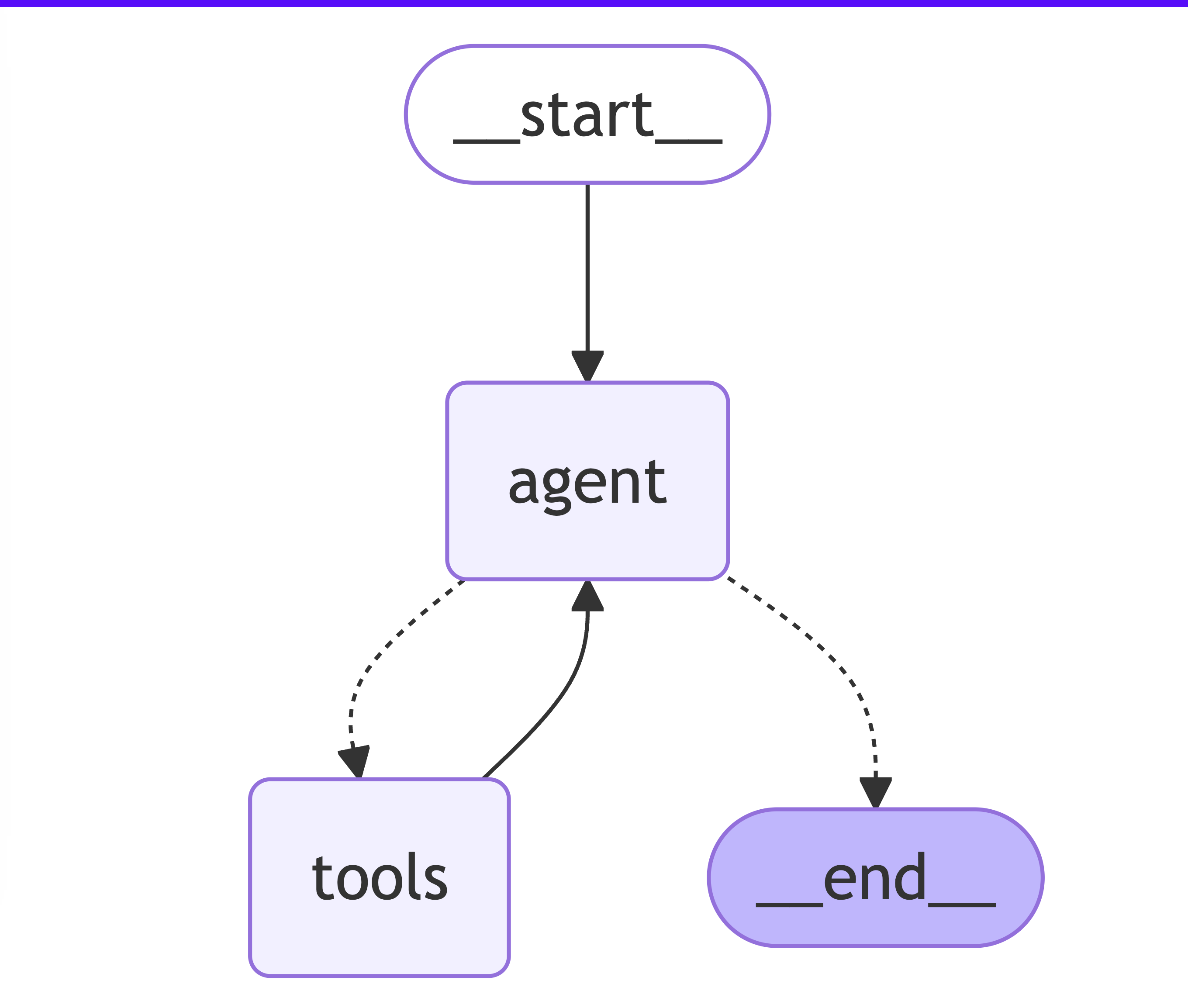
const graph = new StateGraph(MessagesAnnotation)
.addNode("agent", callModel)
.addNode("tools", toolNodeForGraph)
.addEdge("__start__", "agent")
.addConditionalEdges("agent", shouldContinue)
.addEdge("tools", "agent")
.compile();
const inputs = {
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "what is the weather in SF?" }]
};
const graphImg =( await graph.getGraphAsync())?.drawMermaid()
console.log('=======merchantid=====start==');
console.log(graphImg);
console.log('=======merchantid=====end==');
const stream = await graph.stream(inputs, {
streamMode: "values"
});
for await (const { messages } of stream) {
console.log(messages);
}
// Returns the messages in the state at each step of execution
}
下面是输出
[
// 第一步:用户输入
HumanMessage {
"id": "94b78bd3-42cb-4489-84c9-50bf5766eaa8",
"content": "what is the weather in SF?",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {}
},
// 第二步:基于 LLM 得到返回的 AI Message; 即获取到定位信息为 San Francisco
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-BCmEAklWcybBrHURQsDspoY8uGBqv",
"content": "",
"additional_kwargs": {
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_gqkKyGeA2md2fWWKEh6uekpf",
"type": "function",
"function": "[Object]"
}
]
},
"response_metadata": {
"tokenUsage": {
"promptTokens": 61,
"completionTokens": 16,
"totalTokens": 77
},
"finish_reason": "tool_calls",
"model_name": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125"
},
"tool_calls": [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"args": {
"location": "San Francisco"
},
"type": "tool_call",
"id": "call_gqkKyGeA2md2fWWKEh6uekpf"
}
],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"usage_metadata": {
"output_tokens": 16,
"input_tokens": 61,
"total_tokens": 77,
"input_token_details": {
"audio": 0,
"cache_read": 0
},
"output_token_details": {
"audio": 0,
"reasoning": 0
}
}
},
// 第三步:调用 getWeather 工具,获取天气信息
ToolMessage {
"id": "78e84fdc-6697-4071-b439-2679bdb4343d",
"content": "It's 60 degrees and foggy.",
"name": "get_weather",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {},
"tool_call_id": "call_gqkKyGeA2md2fWWKEh6uekpf"
},
// 第四步:由于edge 定义,tool 执行后,下一个为agenet , 将工具的结果返回给 LLM 模型,触发 LLM 模型的第二次调用
AIMessage {
"id": "chatcmpl-BCmEBCY6CzVIME25oFfXR9MTS5Vbl",
"content": "The weather in San Francisco is currently 60 degrees and foggy.",
"additional_kwargs": {},
"response_metadata": {
"tokenUsage": {
"promptTokens": 93,
"completionTokens": 16,
"totalTokens": 109
},
"finish_reason": "stop",
"model_name": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0125"
},
"tool_calls": [],
"invalid_tool_calls": [],
"usage_metadata": {
"output_tokens": 16,
"input_tokens": 93,
"total_tokens": 109,
"input_token_details": {
"audio": 0,
"cache_read": 0
},
"output_token_details": {
"audio": 0,
"reasoning": 0
}
}
}
]
# 使用 createReactAgent 实现简单的天气查询
createReactAgent 已经将 ToolNode + LLM 的实现封装成了一个方法,我们只需要传入工具列表,就可以创建一个 Agent 应用。 简单而言:createReactAgent 内置了 ToolNode、StateGraph(Node/Edge/Annotation)、compile
# createReactAgent 源码
# 实现天气查询
和上面手动编写 ToolNode+Agent 一样的效果和输出;但代码量减少了很多
import { StateGraph, MessagesAnnotation } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { createReactAgent, ToolNode } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
export async function main() {
// 手动顶一个tool
const getWeather = tool(
input => {
if (["sf", "san francisco"].includes(input.location.toLowerCase())) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy.";
} else {
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny.";
}
},
{
name: "get_weather",
description: "Call to get the current weather.",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("Location to get the weather for.")
})
}
);
const tools = [getWeather];
const agent = createReactAgent({
llm: new ChatOpenAI({
temperature: 0,
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
maxTokens: 600
}),
tools: tools
});
const inputs = {
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "what is the weather in SF?" }]
};
const graph = await agent.getGraphAsync();
const graphImg = graph?.drawMermaid();
console.log(graphImg);
const stream = await agent.stream(inputs, {
streamMode: "values"
});
for await (const { messages } of stream) {
console.log(messages);
}
// Returns the messages in the state at each step of execution
}
# 使用 createReactAgent 实现多workflow
import { createReactAgent, ToolNode } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { Annotation, StateGraph, END, START } from "@langchain/langgraph";
async function getDistanceFromChina(location: string) {
// 手动顶一个tool
const getDistance = tool(
input => {
if (input.location.toLowerCase().includes("san francisco")) {
// 这里可以使用高德的 MCP server 获取距离
return "It's 1000 km";
} else {
return "It's 0 km";
}
},
{
name: "get_distance",
description: "Call to get the distance from the location to Chengdu China.",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("Current Location to get the distance for.")
})
}
);
const tools = [getDistance];
const agent = createReactAgent({
llm: new ChatOpenAI({
temperature: 0,
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
maxTokens: 600
}),
tools: tools,
prompt: ""
});
const inputs = {
messages: [{ role: "user", content: `what is the Distance from ${location} to Chengdu, China` }]
};
const graph = await agent.getGraphAsync();
const graphImg = graph?.drawMermaid();
const stream = await agent.stream(inputs, {
streamMode: "values",
// subgraphs: true
});
let result = "";
for await (const { messages } of stream) {
console.log("response= ", messages[messages.length - 1]?.content);
result = messages[messages.length - 1]?.content;
}
// 只返回最后的输出
return result;
}
async function getWether(location: string) {
// 手动顶一个tool
const getWeather = tool(
input => {
if (["sf", "san francisco"].includes(input.location.toLowerCase())) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy.";
} else {
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny.";
}
},
{
name: "get_weather",
description: "Call to get the current weather.",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("Location to get the weather for.")
})
}
);
const tools = [getWeather];
const agent = createReactAgent({
llm: new ChatOpenAI({
temperature: 0,
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
maxTokens: 600
}),
tools: tools
});
const inputs = {
messages: [{ role: "user", content: `what is the weather in ${location}` }]
};
const graph = await agent.getGraphAsync();
const graphImg = graph?.drawMermaid();
const stream = await agent.stream(inputs, {
streamMode: "values",
// subgraphs: true
});
let result = "";
for await (const { messages } of stream) {
result = messages[messages.length - 1]?.content;
}
// 只返回最后的输出
return result;
}
export async function main() {
const StateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
location: Annotation<string>(),
messages: Annotation<string[]>({
default: () => [],
reducer: (current, updated) => {
return Array.from(new Set(current.concat(updated)));
}
})
});
// 创建工作流
const workflow = new StateGraph(StateAnnotation);
workflow.addNode("weather", async state => {
const weather = await getWether(state.location);
return {
messages: [weather]
};
});
workflow.addNode("distance", async state => {
const weather = await getDistanceFromChina(state.location);
return {
messages: [weather]
};
});
workflow.addEdge(START, "weather");
workflow.addEdge(START, "distance");
workflow.addEdge("weather", END);
workflow.addEdge("distance", END);
const graph = await workflow.compile();
const graphStructure = await graph.getGraphAsync();
const graphImg = graphStructure?.drawMermaid();
console.log("=======merchantid=====start==");
console.log(graphImg);
console.log("=======merchantid=====end==");
const stream = await graph.stream(
{ location: "SF" },
{
streamMode: "values",
}
);
let result = "";
for await (const { messages } of stream) {
result = messages;
}
console.log("=======result=========");
console.log(result);
}
# 使用 StateGraph 实现单 workflow调用多agent+tools
import { createReactAgent, ToolNode } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { Annotation, StateGraph, END, START, MessagesAnnotation, messagesStateReducer, Command } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { BaseMessage, HumanMessage, isAIMessage, ToolMessage } from "@langchain/core/messages";
function getDistanceFromChina(location: string) {
const DistanceStateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
distanceMessages: Annotation<BaseMessage[]>({
default: () => [
new HumanMessage({
content: `what is the Distance from ${location} to Chengdu, China`
})
],
reducer: messagesStateReducer
})
});
// 手动顶一个tool
const getDistance = tool(
async (input, config) => {
if (input.location.toLowerCase().includes("san francisco")) {
// 这里可以使用高德的 MCP server 获取距离
return new Command({
update: {
distanceMessages: [
new ToolMessage({
content: "It's 1000 km",
tool_call_id: config.toolCall.id
})
]
}
});
} else {
/**
* 注意!!! 如果是由Agent 调用的 并行任务,这里的返回值需要使用 Command 完成,不能直接返回一个 字符串,否则会报错
*/
return new Command({
update: {
distanceMessages: [
new ToolMessage({
content: "It's 0 km",
tool_call_id: config.toolCall.id
})
]
}
});
}
},
{
name: "get_distance",
description: "Call to get the distance from the location to Chengdu China.",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("Current Location to get the distance for.")
})
}
);
const tools = [getDistance];
const modelWithTools = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature: 0,
maxTokens: 600
}).bindTools(tools);
// 工具的集合
const toolNodeForGraph = new ToolNode(tools);
const shouldContinue = (state: typeof DistanceStateAnnotation.State) => {
const { distanceMessages = [] } = state;
const messages = distanceMessages;
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1];
if (isAIMessage(lastMessage) && (!lastMessage.tool_calls || lastMessage.tool_calls.length === 0)) {
return END;
} else {
return "continue";
}
};
const callModel = async (state: typeof DistanceStateAnnotation.State) => {
const { distanceMessages } = state;
const response = await modelWithTools.invoke(distanceMessages);
// response.additional_kwargs["message_type"] = "distance";
return { distanceMessages: response };
};
return {
callModel,
toolNodeForGraph,
shouldContinue,
DistanceStateAnnotation
};
}
function getWether(location: string) {
const WeatherStateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
weatherMessages: Annotation<BaseMessage[]>({
default: () => [
new HumanMessage({
content: `what is the weather in ${location}`
})
],
reducer: (current, updated) => {
return Array.from(new Set(current.concat(updated)));
}
})
});
// 手动顶一个tool
const getWeather = tool(
async (input, config) => {
if (["sf", "san francisco"].includes(input.location.toLowerCase())) {
/**
* 注意!!! 如果是由Agent 调用的 并行任务,这里的返回值需要使用 Command 完成,不能直接返回一个 字符串,否则会报错
*/
return new Command({
update: {
weatherMessages: [
new ToolMessage({
content: "It's 60 degrees and foggy.",
tool_call_id: config.toolCall.id
})
]
}
});
} else {
return new Command({
update: {
weatherMessages: [
new ToolMessage({
content: "It's 90 degrees and sunny.",
tool_call_id: config.toolCall.id
})
]
}
});
}
},
{
name: "get_weather",
description: "Call to get the current weather.",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("Location to get the weather for.")
})
}
);
const tools = [getWeather];
const modelWithTools = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
temperature: 0,
maxTokens: 600
}).bindTools(tools);
// 工具的集合
const toolNodeForGraph = new ToolNode(tools);
const shouldContinue = (state: typeof WeatherStateAnnotation.State) => {
const { weatherMessages } = state;
const messages = weatherMessages;
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1];
if (isAIMessage(lastMessage) && (!lastMessage.tool_calls || lastMessage.tool_calls.length === 0)) {
console.log("===weather===lastMessage===== END");
return END;
} else {
return "continue";
}
};
const callModel = async (state: typeof WeatherStateAnnotation.State) => {
const { weatherMessages } = state;
const messages = weatherMessages;
const response = await modelWithTools.invoke(messages);
// response.additional_kwargs["message_type"] = "wether";
return { weatherMessages: response };
};
return {
callModel,
toolNodeForGraph,
shouldContinue,
WeatherStateAnnotation
};
}
export async function main() {
const location = "SF";
const weather = getWether(location);
const distance = getDistanceFromChina(location);
const StateAnnotation = Annotation.Root({
location: Annotation<string>(),
...weather.WeatherStateAnnotation.spec,
...distance.DistanceStateAnnotation.spec,
result: Annotation<string>()
});
// 创建工作流
const workflow = new StateGraph(StateAnnotation);
workflow.addNode("weather_agent", weather.callModel);
/**
* 注意事项!!!
* 如果N个ToolNode并行调用,则不能直接使用 callModel 自动调用 tools 的形式
* workflow.addNode("weather_tools", weather.toolNodeForGraph);
* 原因是 ToolNode 源码默认消费的是 state 中的 messages 字段,而实际上是没有这个字段的(因为不同的agent使用不同的message字段存储)
* 所以需要读取上下文数据后 自定义调用 invoke 方法,并解析出内部的数据
*
*/
workflow.addNode("weather_tools", async state => {
const data: Command[] = await weather.toolNodeForGraph.invoke(state.weatherMessages);
//data = [
// Command {
// lg_name: 'Command',
// lc_direct_tool_output: true,
// graph: undefined,
// update: { weatherMessages: [Array] },
// resume: undefined,
// goto: []
// }
// ]
const merges = data?.map(ele => ele.update?.weatherMessages) || [];
const weatherMessages: any = [];
merges.forEach(ele => {
if (Array.isArray(ele)) {
weatherMessages.push(...ele);
}
});
return {
weatherMessages: weatherMessages
};
});
workflow.addNode("distance_agent", distance.callModel);
workflow.addNode("distance_tools", async state => {
const data: Command[] = await distance.toolNodeForGraph.invoke(state.distanceMessages);
//data = [
// Command {
// lg_name: 'Command',
// lc_direct_tool_output: true,
// graph: undefined,
// update: { distanceMessages: [Array] },
// resume: undefined,
// goto: []
// }
// ]
const merges = data?.map(ele => ele.update?.distanceMessages) || [];
const messages: any = [];
merges.forEach(ele => {
if (Array.isArray(ele)) {
messages.push(...ele);
}
});
return {
distanceMessages: messages
};
});
workflow.addNode("messgae_wrapper", state => {
return {
result:
state.weatherMessages[state.weatherMessages.length - 1].content +
"\n" +
state.distanceMessages[state.distanceMessages.length - 1].content
};
});
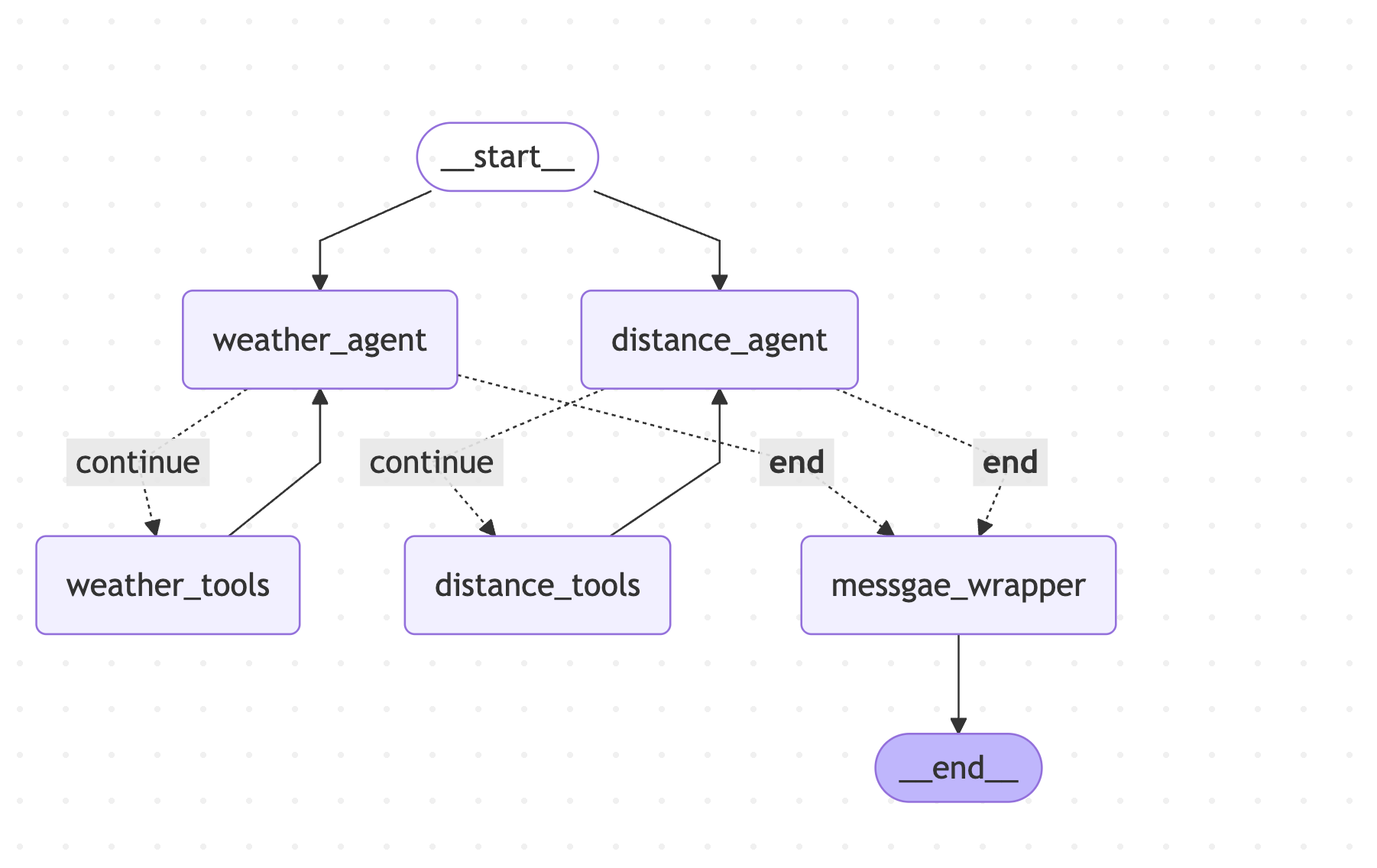
workflow.addEdge(START, "weather_agent");
workflow.addEdge(START, "distance_agent");
workflow.addEdge("weather_tools", "weather_agent");
workflow.addConditionalEdges("weather_agent", weather.shouldContinue, {
continue: "weather_tools",
[END]: "messgae_wrapper"
});
workflow.addEdge("distance_tools", "distance_agent");
workflow.addConditionalEdges("distance_agent", distance.shouldContinue, {
continue: "distance_tools",
[END]: "messgae_wrapper"
});
workflow.addEdge("messgae_wrapper", END);
const graph = await workflow.compile();
const graphStructure = await graph.getGraphAsync();
const graphImg = graphStructure?.drawMermaid();
console.log("=======merchantid=====start==");
console.log(graphImg);
console.log("=======merchantid=====end==");
const stream = await graph.stream(
{
location
},
{
streamMode: "values"
}
);
let res = "";
for await (const state of stream) {
res = state.result;
// res =
// state.weatherMessages[state.weatherMessages.length - 1].content +
// "\n" +
// state.distanceMessages[state.distanceMessages.length - 1].content;
// console.log("distanceMessages====== ", distanceMessages);
// console.log("weatherMessages====== ", weatherMessages);
}
// console.log("=======result=========");
console.log(res);
}
- 本文链接: https://mrgaogang.github.io/ai/langgraph/LangGraph%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8.html
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
