# 前端offset及scroll及client详解
也许你在编程是遇到过如下疑问?
clientX,clientY,pageX,pageY,offsetX,offsetY,screenX,screenY,clientHeight,offsetHeight,scrollHeight,offsetTop,scrollTop,innerHeight分别代表着什么,怎么判断当前列表是否滑动到底部等一系列的疑问; 没事本文为你一一道来。
本文主要讲解Y轴相关属性,X轴属性可依次类推。
首先我们讲一下 clientX,clientY,pageX,pageY,offsetX,offsetY,screenX,screenY.
# 元素事件的 clientX,clientY,pageX,pageY,offsetX,offsetY,screenX,screenY
每一个元素的事件都存在 clientX,clientY,pageX,pageY,offsetX,offsetY,screenX,screenY。你可以尝试一下:
const el = document.getElementById("content");
if (el) {
el.addEventListener("click", function(evt) {
console.log(evt.offsetX, evt.offsetY);
console.log(evt.clientX, evt.clientY);
console.log(evt.pageX, evt.pageY);
console.log(evt.screenX, evt.screenY);
});
}
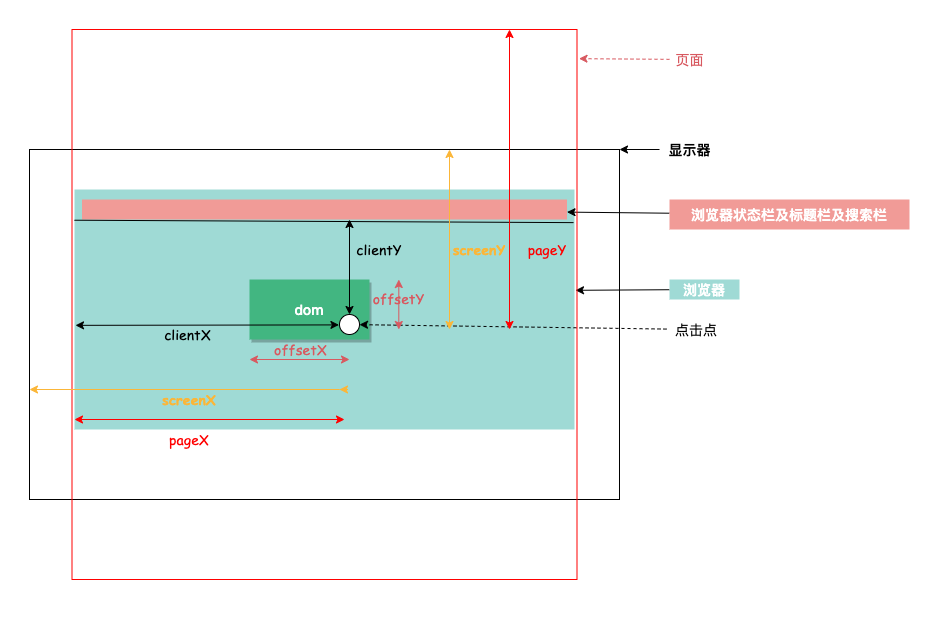
# 1. clientX clientY
鼠标相对于浏览器窗口可视区域的 X,Y 坐标(窗口坐标),表示页面可视区域的 X,Y 偏移量,可视区域不包含工具栏和滚动条,搜索栏等。并且与页面滚动无关,滚动后的 clientY 值不变。
# 2. pageX pageY
类似于 clientX,clientY,但它们使用的是文档坐标而非窗口坐标。页面坐标 Y,与 clientY 基本类似,唯一区别在于该值与页面滚动有关,具体来说,pageY = clientY + 页面滚动高度。
# 3. offsetX offsetY
鼠标相对于事件源元素(srcElement)的 X,Y 坐标。
# 4. screenX screenY
screen 顾名思义是屏幕,是用来获取鼠标点击位置到屏幕显示器的距离,距离的最大值需根据屏幕分辨率的尺寸来计算。
详细内容如下图所示:
# 元素的 clientHeight,offsetHeight,scrollHeight,offsetTop,scrollTop
每一个html元素(包括文档元素document.documentElement)都存在clientHeight,offsetHeight,scrollHeight,offsetTop,scrollTop这几个和元素高度,滚动及位置相关的属性,你可以尝试着使用如下方式进行验证:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.children {
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background-color: pink;
}
#content {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
padding: 10px;
margin: 21px;
border: 2px solid red;
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="content">
<div class="children">children</div>
</div>
<script>
function show(el) {
console.log(el.clientHeight, el.clientWidth); // 120 120
console.log(el.offsetHeight, el.offsetWidth); // 124 124
console.log(el.scrollHeight, el.scrollWidth); // 320 210
console.log(el.offsetTop); // 21
console.log(el.scrollTop); // 0
}
const el = document.getElementById("content");
show(el);
</script>
</body>
</html>
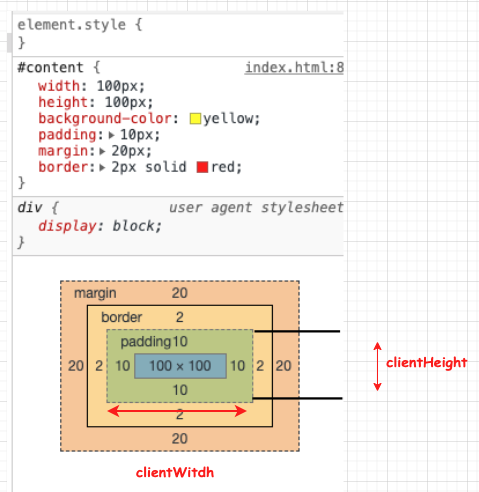
# 1. clientHeight/clientWidth
clientHeight 就是 content 内部
可见高度+ 自身 padding。
包括 padding 但不包括 border、水平滚动条、margin 的元素的高度。对于 inline 的元素这个属性一直是 0,单位 px,只读属性。
clientHeight = CSS height + CSS padding - 水平滚动条高度 (如果存在)
clientWidth = CSS width + CSS padding - 垂直滚动条高度 (如果存在)
回到上面的例子:返回结果为 120 = css height(100) + padding (2* 10)
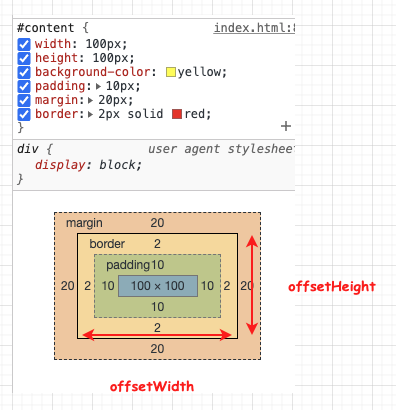
# 2. offsetHeight/offsetWidth
offsetHeight 也是 content 自己本身的可见高度 + 自身 padding + 自身 border + 滚动条
包括padding、border、水平滚动条,但不包括margin 的元素的高度, 不包含:before 或:after 等伪类元素的高度。对于 inline 的元素这个属性一直是 0,单位 px。
offsetHeight = CSS height + CSS padding + 水平滚动条高度 (如果存在) + border 高度
offsetWidth = CSS width + CSS padding + 垂直滚动条高度 (如果存在) + border 高度
回到上面的例子:返回结果为 124 = css height(100) + padding (2* 10) + border (2*2)
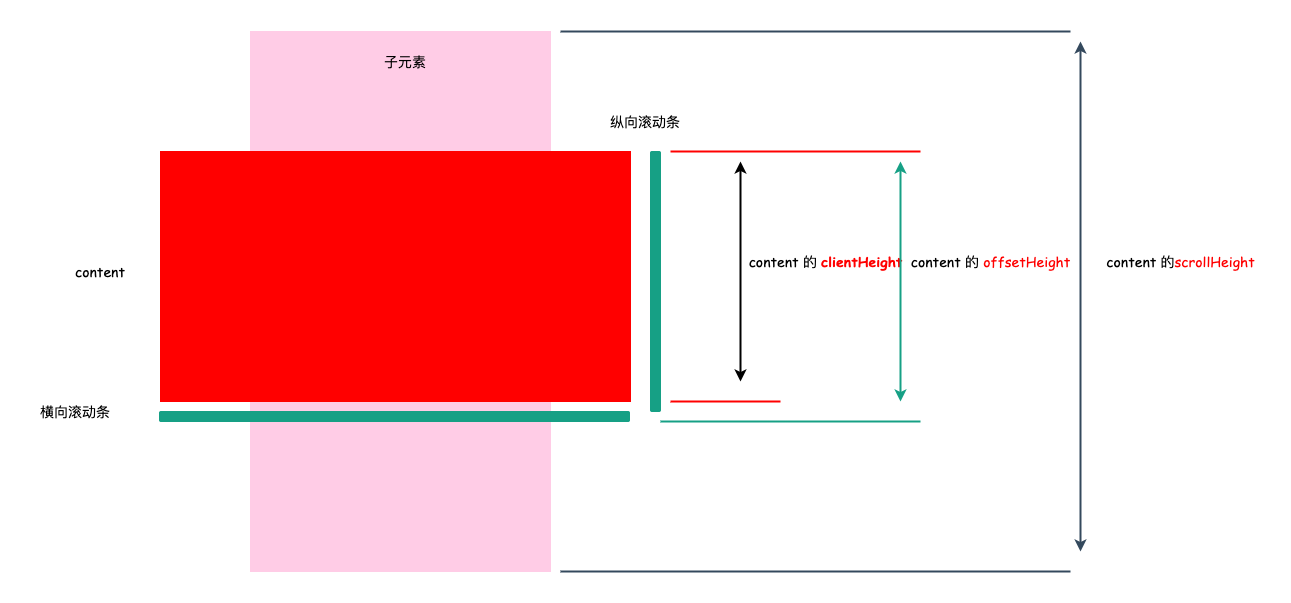
# 3. scrollHeight/scrollWidth
scrollHeight表示实际内容的高度。
没有垂直滚动条的情况下:
scrollHeight === clientHeight。包括元素的 padding,但不包括元素的 border 和 margin。scrollHeight 也包括 ::before 和 ::after 这样的伪元素;有垂直滚动条的情况下: scrollHeight = 子元素的高度 + 当前元素的 padding 高度
回到上面的例子:返回结果为 320 = 子元素 height(300) + 当前元素的 padding (2* 10)
其实 document 也有一个特殊的 scrollHeight: document.documentElement.scrollHeight
表示整个 document 实际内容的高度。
# 4. scrollTop
代表在有滚动条时,滚动条向下滚动的距离也就是元素顶部被遮住部分的高度。在没有滚动条时 scrollTop==0 恒成立,可读可设置
scrollTop 可以被设置为任何整数值,同时注意:
- 如果一个元素不能被滚动(例如,它没有溢出,或者这个元素有一个"non-scrollable"属性), scrollTop 将被设置为 0。
- 设置 scrollTop 的值小于 0,scrollTop 被设为 0
- 如果设置了超出这个容器可滚动的值, scrollTop 会被设为最大值。
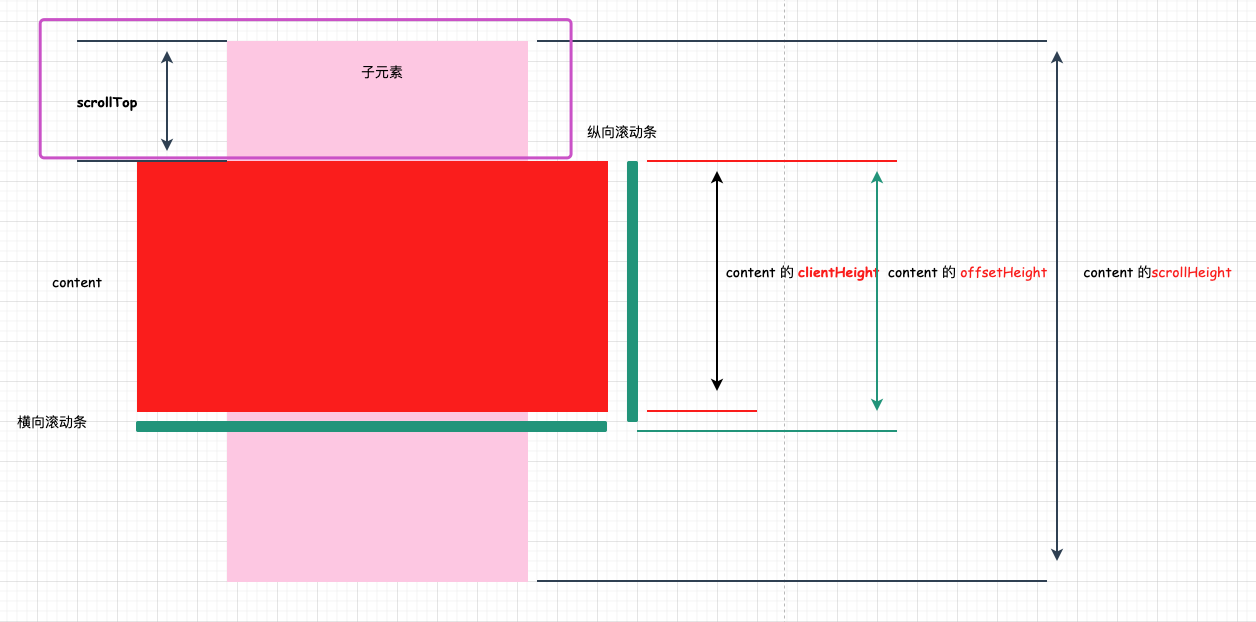
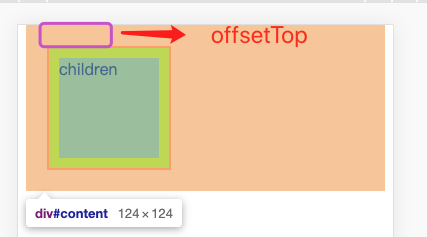
# 5. offsetTop
当前元素顶部 border 外层距离最近父元素内容顶部的距离,与滚动条无关。
回到上面的例子:offsetTop 返回结果为 21 = 元素 content border 距离 body 的距离。
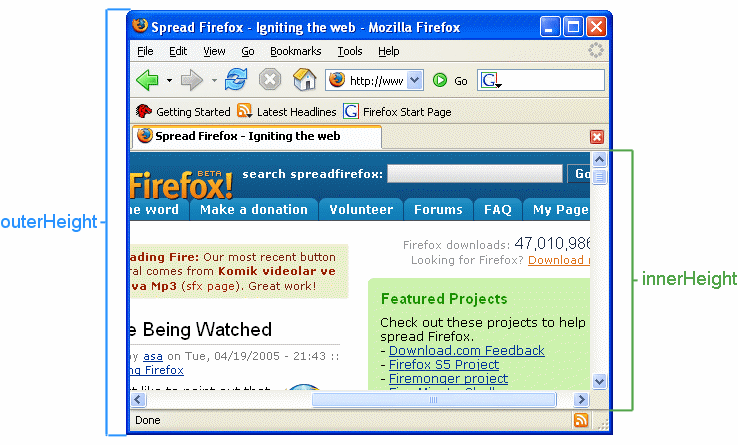
# window.innerHeight/outerHeight/scrollY/scrollX
# 1. window.innerHeight
浏览器窗口的视口(viewport)高度(以像素为单位);如果有水平滚动条,也包括滚动条高度。
# 2. window.outerHeight
window.outerHeight 获取整个浏览器窗口的高度(单位:px),包括侧边栏(如果存在)、窗口镶边(window chrome)和窗口调正边框(window resizing borders/handles)
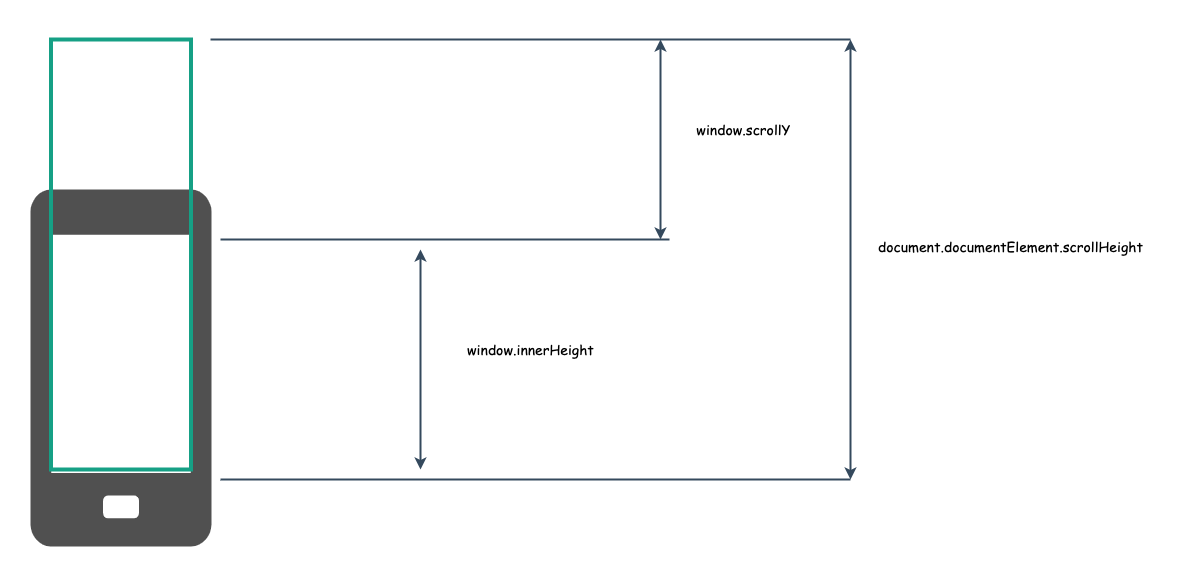
# 3. window.scrollY/scrollX
- window.scrollY 表示document 在垂直方向上滚动的距离;
- window.scrollX 表示document 在水平方向上滚动的距离;
# 如何判断一个元素是否滑动到底部了?
前提:你的子内容高度>当前元素高度
前面已经介绍了 scrollHeight,scrollTop,clientHeight,我们发现判断内部元素是否滑动到底部可以使用如下贡献进行判断:
element.scrollHeight - element.scrollTop === element.clientHeight;
// 一个样例
const el = document.getElementById("content");
el.addEventListener("scroll", function() {
if (el.scrollHeight - el.scrollTop === el.clientHeight) {
console.log("到底咯");
}
});
# 如何判断网页是否滑动到窗口/手机底部了?
前提:你的内容高度>手机窗口高度
我们先简单画一个草图:
实验一下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#children {
width: 200px;
height: 3000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="children">children</div>
<script>
const windowHeight = window.innerHeight;
// 记得做onscroll的防抖/节流哦
window.onscroll = function() {
const documentHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight;
// 可以适当增加距离底部的buff
if (documentHeight <= window.scrollY + windowHeight) {
console.log("滑动到手机底部咯");
}
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 本文链接: https://mrgaogang.github.io/javascript/base/%E5%89%8D%E7%AB%AFoffset%E5%8F%8Ascroll%E5%8F%8Aclient%E8%AF%A6%E8%A7%A3.html
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
